Most people who have an interest in the history of dancing will have heard of the 18th-century French ballerina Marie Sallé. How many will know of Francis Sallé, her brother, who is mentioned only in passing in the various accounts of her career? I use the English form of his first name because, unlike Marie, he chose to pursue a career on the London stage.
Francis and Marie Sallé made their debuts together on the London stage, at the Lincoln’s Inn Fields Theatre on 18 October 1716. They were billed as ‘two Children, Scholars of M Ballon, lately arriv’d from the Opera at Paris’, with the warning to prospective audiences that ‘Their Stay will be short in England’. The ‘Opera’ was, of course, Paris’s Opéra-Comique rather than the Académie Royale de Musique, despite the link with Claude Ballon. Francis is generally said to have been born in 1705 and Marie in 1707, so they were eleven and nine years old when they first came to London. At their first performance, they danced the Harlequins in Two Punchanellos, Two Harlequins and a Dame Ragonde. They proved so popular that their stay was extended. In the bills from 5 to 10 December, Rich encouraged interest in their performances with successive announcements from the children ‘stay but Nine Days longer’ down to ‘the last Time but one of their Dancing during their Stay in England’. Their last performance was, ostensibly, their shared benefit on 11 December 1716, which according to the advertisement in the Daily Courant for that day, included
‘… several Entertainments of Dancing, both Serious and Comic, by the Children and others. A new Comic Dance, call’d The Drunken Man, to be perform’d by the Children. The last New Comic Dance, compos’d by Mons. Moreau, and to be perform’d by him, Mr. Kellom’s Schollar, Mr. Cook, Mrs. Schoolding, Mrs. Cross, Miss Smith, and the Children. Likewise a Scene in the French Andromache burlesqued, to be acted by the Children: Orestes to be perform’d by Mons. Salle, and Hermione by Mademoiselle Salle his Sister.’
On 18 December 1716, the bills announced ‘In Consideration of the Diversion the French Children have given the Town, Mr. Rich has engag’d their Stay in England for some time longer. The two children danced at Lincoln’s Inn Fields until 10 June 1717, with one performance at the King’s Theatre on 5 June, giving more than 100 performances in all. They were allowed a second benefit on 11 May 1717, when they gave a ‘French Scene’ with their father and danced with Moreau and Mrs Schoolding.
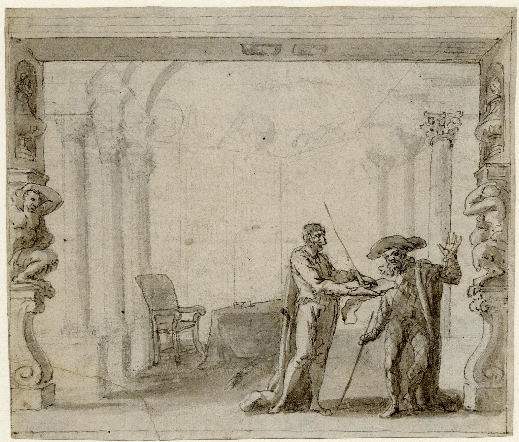
During the 1716-1717 season, the two children performed around a dozen entr’acte dances both serious and comic. Their repertoire included a ball dance by Kellom Tomlinson, The Submission first given on 21 February 1717 and published in notation the same year. The dance opens with a slow triple-time section, followed by a minuet and then a rigadon. Here is the first plate.
This is the only dance created for either Francis or Marie Sallé that survives in notation.
The two young dancers returned to London for the 1718-1719 season, this time appearing first at Lincoln’s Inn Fields and then at the King’s Theatre with the troupe of their uncle Francisque Moylin. At Lincoln’s Inn Fields, they were mentioned only once in the bills, on the 19 December 1718 (their benefit performance), when they were advertised as ‘M and Mlle Salle, the two Children, who dance in the Company of the French Comedians’. They were billed only three times when Moylin’s company moved to the King’s Theatre. However, the Lincoln’s Inn Fields bill suggests that they may have danced at most, if not all, of the 40 performances that the French Comedians gave at the two theatres between 7 November 1718 and 19 March 1719. The bills say nothing at all about their repertoire.
Francis and Marie Sallé did not return to London again until the 1725-1726 season, when they again danced for John Rich at Lincoln’s Inn Fields. By this time, Francis was twenty years old and Marie eighteen and they immediately became the company’s leading dancers. They performed the title roles in that season’s new pantomime, Apollo and Daphne; or, The Burgomaster Trick’d, Rich’s answer to Drury Lane’s Apollo and Daphne; or, Harlequin’s Metamorphoses of the previous season. At Drury Lane, the title roles had been taken by John Thurmond Jr (the pantomime’s creator) and Hester Booth and Rich followed suit with two dancers at Lincoln’s Inn Fields. The two Sallés also appeared as Zephyrus and Flora in the pantomime’s concluding divertissement. Apollo and Daphne; or, The Burgomaster Trick’d, first performed on 14 January 1726, was given 45 performances before the end of the season. Francis Sallé was billed for 106 performances during 1725-1726. As well as dancing four entr’acte duets with Marie, he apparently gave a solo French Sailor (in addition to the French Sailor and His Wife with his sister) and danced Two Pierrots with Francis Nivelon as well as Two Harlequins with Louis Dupré. He also partnered Mrs Bullock in a Grand Dance with other dancers in the company. Francis and Marie Sallé shared a benefit on 18 April 1726, the last time they would do so. Their careers were already beginning to diverge.
Both Sallés returned to Lincoln’s Inn fields for the 1726-1727 season. They were first billed together, without comment, on 19 September 1726 dancing Shepherd and Shepherdess and French Sailors. Francis had already appeared a few days earlier, dancing First Fury in The Necromancer (a role he had initially performed the previous season). He and Marie repeated their roles in Apollo and Daphne and danced together in the entr’actes, although Francis was also billed (without Marie) alongside other dancers in the company for performances of The Prophetess as well as a new masque Pan and Syrinx, first given on 24 October 1726. Later in the season, on 30 May 1727, he was billed as Mezzetin Man (with the actress-dancer Elizabeth Younger as Mezzetin Woman) in The Necromancer as well as First Fury. By contrast, Marie’s only billing without her brother was on 27 April 1727, when she performed a new Ball Dance with Leach Glover at his benefit.
The main reason for the Sallés engagement at Lincoln’s Inn Fields in 1726-1727 was undoubtedly their appearance in the new pantomime, The Rape of Proserpine, introduced on 13 February 1727 and performed 32 times before the end of the season. This was a pantomime that Rich had long wished to produce. In the libretto for Harlequin a Sorcerer, first given at Lincoln’s Inn Fields on 21 February 1725, he had written of ‘The Expectation which has been rais’d in the Town of seeing a Dramatick Entertainment, call’d The Rape of Proserpine‘ explaining that ‘being disappointed of some very necessary Persons from abroad, on whom we depended, we have deferr’d the same for some time longer’. The ‘very necessary Persons’ must have been Francis and Marie Sallé, for all the other principal performers in The Rape of Proserpine appeared in Harlequin a Sorcerer. When Rich was able to engage the two Sallés for the 1725-1726 season, his focus had evidently turned immediately to the need to outdo Drury Lane’s Apollo and Daphne and he had deferred his pet project for another year.
In The Rape of Proserpine, the roles of Ceres, Pluto, Proserpine and Mercury were all performed by singers, although Marie and Francis danced in the serious part of the pantomime. She was the first of five female Sylvans, while he was the first of four Gods of the Woods and the first of five Demons. The most spectacular dancing was probably reserved for the ballet which ended the pantomime, described thus in the libretto, ‘Enter several Dancers, who represent the four Elements, and celebrate the Marriage of Pluto and Proserpine, by a Grand Ballet.’ Earth was danced by Louis Dupré, with Mrs Pelling as his Female. Air was Leach Glover, with Mrs Laguerre, and Fire was Poitier with Mrs Bullock. The ballet must have culminated with the appearance of Francis Sallé as Water, accompanied by his sister. The bills suggest that the men may have danced virtuoso solos as well as duets with their ‘Females’. The Rape of Proserpine drew on Lully’s 1680 opera Proserpine and the ballet of the elements may have had a French source too, although this has yet to be identified.
This season, Marie received her own benefit on 6 April 1727 at which she apparently did not dance, for the advertisement announced only a Pastoral by her scholar the nine-year-old Miss Rogers and Two Pierrots by Francis Nivelon and Francis Sallé. Her brother’s benefit was a week later, on 14 April, at which the mainpiece was The Prophetess (in which he may well have danced) and the dancing comprised a solo Harlequin by Miss Violante, his scholar, a solo version of Les Caractères de la Dance by Marie and a Fury Dance with Francis as First Fury (presumably taken from The Necromancer). It is worth noting that Marie’s benefit was more profitable than that of Francis and had higher attendance than his. Marie Sallé had already emerged as the more celebrated dancer and was probably the more ambitious too. During 1726-1727, Francis Sallé gave 97 performances and had evidently decided that his future lay with Rich’s company. The surviving Lincoln’s Inn Fields accounts for that season record a payment of 10 guineas on 9 June 1727 to ‘Mr Salle upon signing articles and in pt of next year’s contract’.
Marie Sallé would not return to London and Lincoln’s Inn Fields until the 1730-1731 season. Francis became one of Rich’s group of dancers, although he probably returned to dance in France regularly. His first London season without his sister, 1727-1728, may not have met his expectations. On 29 January 1728, the first performance of The Beggar’s Opera was given at Lincoln’s Inn Fields, and the production dominated the theatre’s repertoire until the end of the season. None of the bills for The Beggar’s Opera mention dancing, but the libretto does refer to dances and it is possible that at least one of them – the ‘Dance of Prisoners in Chains’ was performed by male dancers in the company. Otherwise, Francis Sallé was billed only four times in the entr’actes, although his appearances in The Necromancer, Apollo and Daphne and The Rape of Proserpine (with Mrs Laguerre in Marie Sallé’s roles in the two latter pantomimes) came to a total of 46 performances. His benefit, on 22 April 1728, was shared with Michael Poitier and he did not dance himself. Sallé’s last billing before that was on 25 March 1728 and he may have been absent for the rest of the season.
Although The Beggar’s Opera was given frequently in 1728-1729, there was more room for other repertoire in the course of the season. Francis Sallé danced from 21 October 1728 to 22 May 1729 and was billed in three entr’acte duets, two entr’acte group dances and five afterpieces (three of which were pantomimes). He was advertised in 67 performances altogether and allowed a solo benefit on 8 April 1729, when he danced the Mad Soldier in The Humours of Bedlam (a comic ballet always given with the play The Pilgrim) as well as two entr’acte duets with Mrs Laguerre – Highlander and Mistress and French Sailor. By this time he had established a dance partnership with Mrs Laguerre, their new duet Highlander and Mistress was repeated nine times before the end of the season and continued to be popular thereafter.
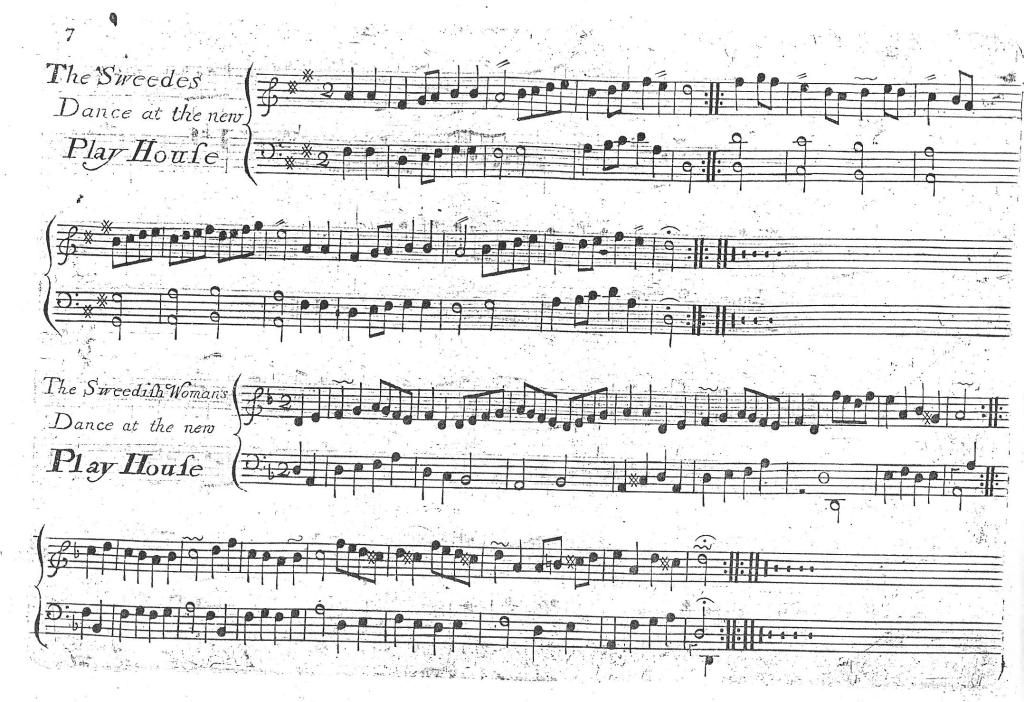
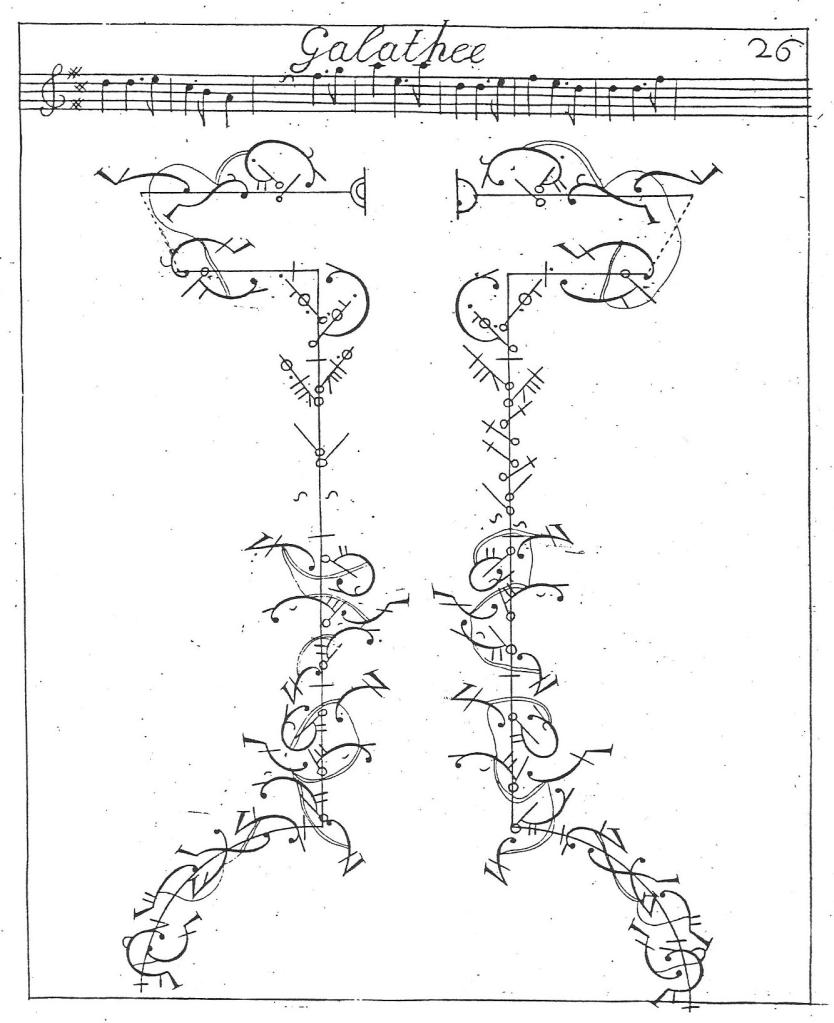
In 1729-1730, Sallé was billed for 117 performances. This season was dominated by another new pantomime, Perseus and Andromeda; or, The Cheats of Harlequin (or, The Flying Lovers), Rich’s response to Drury Lane’s Perseus and Andromeda: With the Rape of Colombine; or, The Flying Lovers by Roger and Weaver given the previous season. The Lincoln’s Inn Fields Perseus and Andromeda was performed 60 times before the end of 1729-1730. Francis Sallé was an Infernal in the serious part of the pantomime, for which Rich had drawn on Lully’s 1682 opera Persée, and it is tempting to speculate whether he and his fellow dancers (Poitier, Dupré, Pelling, Newhouse and Lanyon – Papillion, billed first, was actually a singer and probably did not dance) performed to the ‘Entrée des Divinités Infernales’ from the opera. A duet created by Guillaume-Louis Pecour to this music for Marcel and Gaudrau, performed at the Paris Opéra, was published in notation around 1713 and shows the demands that could be placed on male dancers at the period. Sallé’s early tuition by Claude Ballon (which could have continued beyond his childhood) indicates that he might well have been capable of similar virtuosity. Here is the first plate:

Sallé also danced in a smaller scale afterpiece in 1729-1730, The Dutch and Scotch Contention first given on 29 October 1729. This was probably taken from a ballet performed at the Opéra-Comique in Paris, in which Sallé had appeared ‘en Ecossois’ alongside Roger and Nivelon. I looked at this piece in some detail in my post Highland Dances on the London Stage, back in February 2021. Sallé’s duet Highlander and Mistress with Mrs Laguerre formed part of the action in the London ballet.
Marie Sallé returned to Lincoln’s Inn Fields for the 1730-1731 season, first appearing on 23 November 1730 and dancing until 4 June 1731. Francis made his first appearance some two months before the arrival of his sister, on 21 September 1730, and his last just a few days later, on 7 June 1731. His benefit was on 5 April 1731, in which he danced The Loyal and Generous Free-Mason with Dupré, Pelling and Newhouse – described in the advertisements as ‘all Brothers’- as well as the duets Les Caractères de la Dance and the Louvre and Bretagne with Marie. The last two were ballroom dances by Guillaume-Louis Pecour, among the most famous choreographies of the day and regularly given at benefit performances in London’s theatres. Sallé’s benefit brought in a little over £129. His sister’s benefit, held on 25 March 1731 and commanded by the King (who attended with the Queen, Prince William and the ‘three eldest princesses’), brought in more than £194. She and Francis performed Les Caractères de la Dance together, while Francis also contributed a Scottish Dance duet with Mrs Laguerre (perhaps the popular Highlander and Mistress introduced in 1729).
During 1730-1731, Francis danced with his sister at only 16 of his 50 appearances in the entr’actes and at only 22 of his 65 afterpiece performances. He danced with Marie in Apollo and Daphne and The Rape of Proserpine, but his most popular entr’acte dance was again Highlander and Mistress with Mrs Laguerre. While their respective benefits underlined Marie Sallé’s celebrity status, Francis demonstrated his independence from his sister and his importance as a dancer on the London stage.
The 1731-1732 season was marked by the absence of Marie Sallé. Francis danced at Lincoln’s Inn Fields from 4 October 1731 to 2 June 1732, giving 111 performances in all. His benefit on 12 April 1732 brought in a little over £80 and he was allowed a second benefit on 24 May 1732 which achieved receipts of just over £93. The receipts and the two benefits (an unusual arrangement) need analysis which I won’t undertake here, although there is no question that Francis Sallé was working hard for John Rich who certainly appreciated his contribution to the company. This season, his principal partner was Mrs Laguerre, with whom he performed several entra’cte dances including French Sailor and Wife (presumably the duet Francis had often performed with his sister), Highlander and Mistress and a new duet The Baulk which promised to be popular beyond 1731-1732. He again took leading dancing roles (partnering Mrs Laguerre) in Apollo and Daphne, The Rape of Proserpine and The Dutch and Scotch Contention. For his final performance of the season, Sallé danced as an Infernal in Perseus and Andromeda.
Just ten days after his last performance, the Daily Post for 12 June 1732 announced that:
‘On Friday last died at his Lodgings at Newington Green, after a tedious Indisposition, Mons. Salle, a celebrated Dancer belonging to Lincoln’s Inn Fields Playhouse.’
Francis Sallé was buried at St. John Hackney on 14 June 1732. He was little more than twenty-seven years old. According to Dacier in Une Danseuse de l’Opéra sous Louis XV (pp. 293-4), Marie Sallé was grief-stricken by her brother’s death and a portrait of Francis was found among her possessions after her own death.
Francis and Marie Sallé pursued separate careers alongside their performances together in London. She was far more successful, yet his career deserves much more attention than it has received. He was, for a time, the leading male dancer in John Rich’s company at Lincoln’s Inn Fields and – had he lived longer – would undoubtedly have gone on to star at the first Covent Garden Theatre, opened by Rich in December 1732 just a few months after Sallé’s untimely death.
Notes:
In his biography, Une Danseuse de l’Opéra sous Louis XV: Mlle Sallé (1707-1756), Émile Dacier gives her birth year as 1707 (p. 4 n. 2). Evidence has recently been published that Marie Sallé was in fact born in 1709 (see Robert Kenny, Monsieur Francisque’s Touring Troupe (Woodbridge, 2025), p. 8). In their Mémoires pour servir à l’histoire des spectacles de la foire, 2 vols. (Paris, 1743) the Parfaicts declare that Francis was two years older than Marie (vol. 1, p. 207), which suggests that he might have been born in 1707 although his birth year is still being cited in modern sources as 1705.
For The Rape of Proserpine, Perseus and Andromeda and French dancing see: Moira Goff, ‘John Rich, French Dancing, and English Pantomimes’, “The Stage’s Glory” John Rich, 1692-1761, ed. Berta Joncus and Jeremy Barlow (Newark, NJ, 2011), 85-98.
There are numerous volumes of accounts for the Lincoln’s Inn Fields and Covent Garden theatres during the 18th century in the manuscript collections at the British Library. The entry for Francis Sallé quoted above comes from Egerton ms. 2266, f. 171r.
For dancing in The Beggar’s Opera, see Jeremy Barlow and Moira Goff, ‘Dancing in Early productions of The Beggar’s Opera’, Dance Research, 33.2 (2015), 143-158 (pp. 148-149 for the ‘Dance of Prisoners in Chains’).
Other Dance in History posts relating to the London career of Francis Sallé include:
Aimable Vainqueur on the London Stage
La Bretagne in London
Highland Dances on the London Stage
The Humours of Bedlam
The Necromancer at 300
Season of 1725-1726 (11 posts on various aspects of the dancing at Drury Lane and Lincoln’s Inn Fields this season)